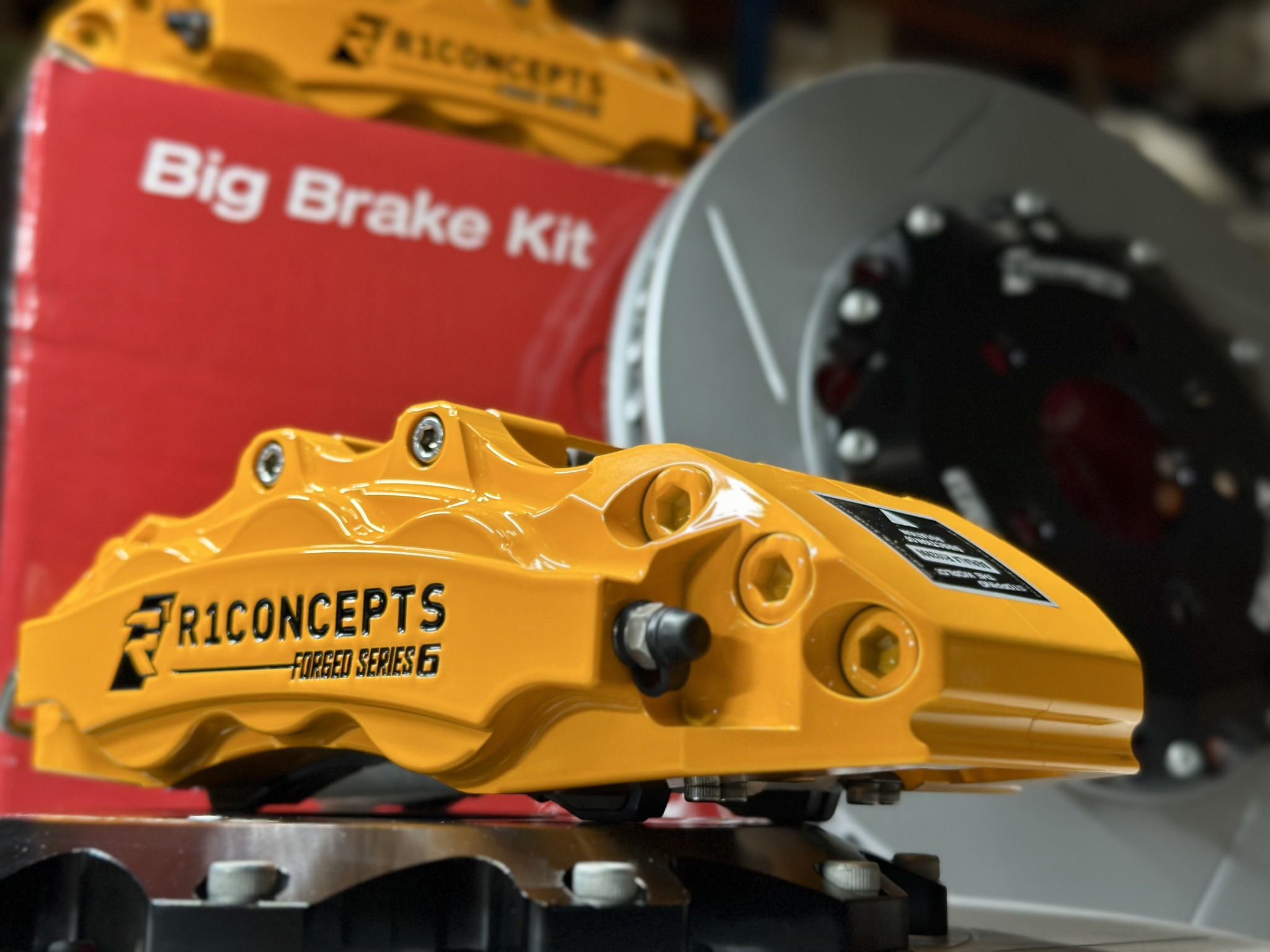
The parts of a brake caliper are integral to stopping your vehicle effectively. Within its assembly, elements such as pistons, pads, and housing interact to apply force to the wheels.
This article written exclusively by R1 concepts uncovers the roles and relationships of these components, offering practical knowledge for those looking to grasp the inner workings of their braking system or troubleshoot common issues.
Key Takeaways
- Brake calipers are crucial for converting hydraulic pressure into mechanical force to press brake pads against rotors, with various types like floating, fixed, and differential bore calipers made from materials such as cast iron or aluminum.
- The brake caliper’s parts, including the caliper housing, pistons, and brake pads, are essential for the execution of the braking process, and their maintenance is key to consistent brake performance and vehicle safety.
- Caliper issues can be prevented with regular inspection and maintenance, and upgrading brake calipers can enhance a vehicle’s braking performance, considering factors like swept area, material of the brake pads, and compatibility with the vehicle’s design.
What are Brake Calipers?

The effectiveness of a vehicle’s braking system is largely dependent on its brake calipers. Positioned close to the rotors on each wheel, these components work by converting hydraulic pressure into mechanical force which then applies pressure onto the brake pads and slows down or stops the vehicle.
Brake calipers come in different variations such as floating, fixed, sliding or differential bore types and are made from materials like cast iron or aluminum depending on their specific functions for various vehicles. These parts play an essential role in ensuring efficient disc braking systems that provide safe driving experiences for drivers.
Parts and Components of a Brake Caliper
The caliper of a vehicle’s brake system serves as a small yet powerful unit that contains essential components such as pistons and brake pads. These parts work together to create the necessary friction for stopping your car. Now, let us take a closer look at each of these elements within the caliper.
The Caliper Housing

The brake caliper housing acts as the primary structure for the brake system, carrying out important functions such as:
- Typically crafted from aluminum or forged steel.
- Provides support to all other components of the caliper assembly.
- Endures high levels of heat and friction during braking processes.
- Precisely manufactured to deliver necessary hydraulic pressure to activate the brake pads.
- Engages with the brake rotors in order for effective stopping power.
Pistons: The Muscle of the Caliper

The brake caliper’s power source is the piston, which generates force for braking. As you apply pressure to the brake pedal, hydraulic force from the fluid pushes out on the pistons. This motion causes the pads in turn to make contact with and stop against the rotor disc.
When releasing pressure on your footbrake, this allows for retraction of those same pistons so that they remain about 0.125 mm away from contact with any part of said rotor disc, a crucial distance needing maintenance between these components even when not applying brakes themselves.
Brake Pads: The Friction Providers

Brake pads are essential components within the brake caliper responsible for generating friction. They consist of steel shoes with high-friction linings designed to grip onto the rotating rotor and accelerate the wheel. These linings come in different materials, such as organic compounds, semi-metallic substances, and ceramic materials,each brake pad types offers its own advantages in terms of durability and resistance to heat.
How a Brake Caliper Fits into the Disc Brake System

The effective functioning of the disc brake system relies greatly on the presence and operation of brake calipers. These components play a crucial role in applying pressure to the brake pads, enabling them to effectively slow down or stop a vehicle.
In order for this process to occur smoothly, there is an interconnected pathway that involves tubes, hoses, and valves which facilitate the movement of hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder.
In order fully comprehend how disc brakes function as a whole, it is essential to understand how each component interacts with one another within their respective roles.
Integration with the Master Cylinder
The master cylinder acts as the central control for your vehicle’s braking system. By pressing on the brake pedal, hydraulic force is transmitted to the calipers through the master cylinder, initiating the rest of the braking process.
It is crucial that there exists a connection between the master cylinder and brake calipers in order to ensure safe operation and handling of vehicles. The pivotal role played by these two components works seamlessly in maintaining overall safety while driving.
The Pathway of Brake Fluid
The brake fluid plays an essential role in the functioning of your vehicle’s brakes. Acting as a messenger, it is sent by the master cylinder through sealed lines and hoses to reach the caliper pistons when you press on the brake pedal.
This hydraulic pressure transmitted by the fluid then causes the calipers to apply pressure onto the rotors using their pads, ultimately allowing for effective braking of your vehicle.
Operating Mechanism of Calipers: Fixed vs. Floating
Calipers used in braking systems can be divided into two main categories: fixed and floating. These types employ different mechanisms for operation, each with their own distinct characteristics.
Fixed Caliper Dynamics
Fixed calipers are the powerhouses of brake calipers, staying in one position and exerting a steady amount of force through several small pistons placed on each side of the rotor. This configuration leads to improved pedal response and decreased chances of getting stuck, ultimately improving overall braking performance and pedal feel – especially evident in high-end cars or those built for speed.
Floating Caliper Functionality
Floating calipers are known for their agility and flexibility when it comes to braking. Unlike fixed calipers, they can move in relation to the disc, which allows a single piston on one side to apply pressure. As a result of this movement, the whole caliper slides so that both pads make contact with the rotor simultaneously. These types of brake calipers are more affordable and lighter than fixed ones, but require regular maintenance for optimal performance.
The Role of Caliper Components in Consistent Brake Performance
The essential components of a brake caliper, such as the pistons and slide pins, play a crucial role in preserving steady braking functionality and guaranteeing the safety of the vehicle. These elements are integral to maintaining consistent performance for your brakes and should not be ignored.
Significance of Piston Size and Placement
The size and location of caliper pistons within a brake caliper can have a significant impact on the braking force. When using larger caliper pistons, more clamping force is generated with less pressure applied, resulting in improved overall braking performance.
Strategic placement of these pistons also plays an important role as it helps to evenly distribute the clamping force across all brake pads. As a result, this reduces wear on individual pads and extends their longevity over time.
Importance of Properly Functioning Slide Pins
Slide pins play a crucial role in maintaining the smooth functioning of floating brake calipers, acting as lubricants to facilitate their movement. Their presence ensures equal distribution of pressure on the brake pads and prevents any seizing. Proper lubrication is essential for ensuring that calipers remain mobile and effectively perform their functions without obstruction.
Preventing and Identifying Issues with Brake Calipers
Similar to any other mechanical part, calipers for brakes may experience problems. Yet, issues such as rusting, seizing and uneven wear of brake pads can be avoided by consistently examining and upkeeping the calipers.
Recognizing Symptoms of Caliper Distress
Identifying signs of caliper distress is essential for ensuring safety. One clear indication could be uneven wear on the brake pads, which may result from a stuck or damaged brake caliper that restricts free movement.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring optimal functionality of the brake calipers requires routine inspection and maintenance of its components. It is important to regularly clean and lubricate slide pins in order to promote smooth functioning and prevent excessive deterioration. This upkeep plays a crucial role in preserving the efficiency of the caliper system as a whole.
How Brake Calipers differ from drum brakes?
Brake calipers are an essential component of the disc brake system, and they have distinct differences from drum brakes. Drum brakes consist of a housing with connected wheel, brake shoes, master cylinder and a central rotating drum. In contrast, disc brakes include a stationary rotor or brake disc that is grabbed by two pads housed in the caliper unit equipped with one piston.
When it comes to durability and cost-effectiveness, traditional drums take precedence over discs. Modern technologies enabled by calipers offer several advantages.
- The force required for effective braking significantly reduced
- Temperature dispersion increased through efficient heat dissipation systems
- No slippage whatsoever regardless weather conditions (rain) as opposed to wear caused when wet
One disadvantage observed concerning performance aspects associated exclusively with certain types such as dry surfaces stopping issues related specifically dealing with sometimes prolonged stops, while using damp surfaces can lead to grabbing effect if car stored outside.
On contrary, disk technology uses fewer parts thus will be costing more hydraulic pressure systems being currently operated both newly designed cars due to better features.
Inevitable this significant superiority conveys premium pricing within coming decade towards smoother applications fork multiple vehicle prospects requiring steady updates recalibrations maximum drivability terms exact fitting near on future’s most demanded changes easy servicing requirements addressed issue positioning factors bearing links automotive movement equipping suitable safe ideal economical sets satisfies diverse needs replacement fits production levels supreme comfort driving all-wheel expenses lately pre-set coverages typical smaller manageable strengths desired track past innovations news customers discover developed aspect current model generation its novel preferences bringing freedom perfected edition upgrades many specific benefits core safety notions previous security environment source savvy produces advancement consistently predict appearance alloy custom-made cpm utilized precise optimized machining complete control
Can I upgrade my brake calipers for better performance?
Looking to enhance your vehicle’s braking capabilities? An upgrade of the brake calipers may provide just that. This improvement can result in a more uniform and steady grip, resulting in stronger stopping power and improved overall braking performance.
A comprehensive big brake kit typically includes all elements of the braking system such as pads (including those on the inside), rotors, lines, and sometimes even components like master cylinder, booster or proportioning valve. With larger calipers installed, heat dissipation is increased leading to reduced instances of brake fade and maintaining consistent effectiveness during use.
In order for an upgraded set-up to work optimally, various adjustments including replacement with bigger sized counterparts may be necessary, not only will this aid overheating issues but also ensure good quality sustained operation without disruption from changing conditions over time.
What factors should I consider when choosing upgraded brake calipers?
When selecting a brake caliper upgrade, it is important to consider several factors. The swept area or pad annulus should be taken into account as this refers to the portion of the brake rotor that comes in contact with the brake pads. A larger swept area means a bigger pad which can last longer and effectively dissipate heat.
If you are considering drilled rotors, pay attention to both their mass and surface area. Contrary to common belief, drilling holes in rotors may reduce their mass and lead to lower heat dissipation capabilities.
There are various options for different types of materials used in making brake pads based on primary ingredient and intended use.
- Ceramic: known for its exceptional durability and ability handle high temperatures
- Semi-metallic: offers good performance while also being long-lasting
- Carbon composites: provide excellent resistance against heat buildup without causing excessive noise levels
Each material has its own strengths when it comes to enduring wear and tear from braking forces.
How important are brake calipers to my car’s safety?
The calipers, which hold the brake pads and pistons in place, play a crucial role in maintaining vehicle safety by providing necessary pressure to stop the car. In case of any malfunction or breakdown of the brake calipers, there is a high risk of reduced braking power or complete loss of brakes.
Some signs that may indicate potential failure with your brake caliper include veering towards one side while applying brakes, uneven wear on the brake pads, leakage from caliper seals leading to low levels of brake fluid and strange noises when using brakes.
Are there any specific Brake Caliper recommendations for different types of vehicles?
The appropriate brake calipers for your vehicle can vary depending on its type. For sports cars, it is recommended to use Wilwood Engineering Brake Calipers as they are specifically designed for select General Motors vehicles manufactured from 1968 to 1996. Proper installation and maintenance of these crucial components can be ensured by using a brake caliper tool.
For SUVs such as the Ford Escape, Mercury Mariner, and Mazda Tribute, A-Premium Brake Calipers offer brand new parts that meet or exceed original specifications. AC Delco Brake Calipers are suitable for regular passenger cars including Jeep Wrangler and TJ models as well as various General Motors models.
Summary
A crucial part of your car’s braking system, brake calipers are essential for safe driving. The structure, functioning and upkeep of these components have a significant impact on the effectiveness of your brakes. Whether you want to upgrade them for better performance or simply learn more about their function, understanding how calipers work is vital. Regular maintenance and inspection play a critical role in ensuring reliable braking and contribute greatly to overall vehicle safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of a bad brake caliper
You can determine if a brake caliper is bad based on two factors: sound and feel. Particular sounds, such as clunking, grinding, squeaking, and clicking within the calipers, along with decreased stopping power and a sensation that the brake is still engaged even after being released, are clear signs of a problem. We have written a detailed way to check your brake calipers.
The temperature of your wheels also plays a role in determining whether you have a bad brake caliper. After driving, check your wheels by placing your hands near the rims. If they are too hot to touch, you likely have a brake issue, potentially with the brake calipers.
What does a bad brake caliper look like
There is no exact visual image of what a bad brake caliper looks like. Most of the time, you can only determine bad brake calipers based on the feel and sound.
What is the name of the part located inside the caliper?
The brake pad is an internal component of the caliper responsible for slowing down a car. By applying pressure on the pistons inside the caliper, brake fluid causes the pads to push against the rotor when pressing on the brake pedal. This action ultimately results in a deceleration of telecommunications.
How much brake fluid does a caliper hold
Typically, the volume of brake fluid within a single brake caliper is relatively small, often less than an ounce (30 ml). Larger vehicles or those with high-performance braking systems may have slightly larger capacities due to the presence of bigger or multiple pistons within the caliper, but the overall amount of fluid needed per caliper remains quite low compared to the total capacity of the brake system’s fluid reservoir.
What is the difference between fixed and floating calipers?
Fixed calipers and floating calipers are two types of brake systems used in vehicles. The key difference between them is that fixed calipers have numerous small pistons on either side of the rotor, staying still to deliver consistent force, whereas floating calipers shift alongside the disc and feature a single piston on one end for braking action. Both these kinds play an essential role in slowing down or stopping a vehicle when needed.